When it comes to designing or understanding a building’s layout, floor plans are the unsung heroes of architectural visualization. A well-crafted house floor plan can communicate volumes about a space, its functionality, and its potential. Whether you’re an aspiring architect, a homeowner planning a renovation, or simply curious about the world of design, mastering the art of floor plans is a valuable skill. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of floor plans, from their importance to tips for creating and interpreting them effectively.
Introduction to House Floor Plans
What Are Floor Plans?
A floor plan is a scaled diagram that depicts the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other architectural elements within a space. It provides a bird’s-eye view of a building’s layout, showcasing the spatial relationships between different areas. House Floor plans are used by architects, designers, builders, and homeowners to visualize and communicate design concepts.
Importance:
House floor plans are the foundation of any architectural project. They serve as a blueprint for construction, guiding builders in accurately implementing the design. Moreover, they help homeowners and clients envision the final outcome and make informed decisions about design choices. Whether it’s a residential home, an office space, or a retail store, a well-designed floor plan can significantly impact the functionality and aesthetics of the space.
Components of a Floor Plan
A house floor plans consist of several essential components that collectively represent the layout of a space:
Walls and Dividers
Walls are represented by lines on a floor plan. Different wall types, such as load-bearing walls or partitions, are usually indicated using distinct line styles.
Doors and Windows
Doors and windows are crucial for determining the flow of movement and the entry of natural light. They are symbolized with specific icons and annotations.
Furniture and Fixtures
Floor plans often include representations of furniture and fixtures to provide a sense of scale and functionality. These elements help visualize how the space is utilized.
Dimensions and Scale
Accurate measurements are critical in house floor plans. Dimensions are typically shown between walls to provide an understanding of the size of different spaces. The scale of the floor plan (e.g., 1/4 inch represents 1 foot) is mentioned to ensure accuracy.
Types of Floor Plans
Residential
Residential house floor plans are tailored to homes and apartments. They include bedrooms, living areas, kitchens, bathrooms, and other domestic spaces. Open floor plans, where spaces flow seamlessly, are popular in modern residential design.
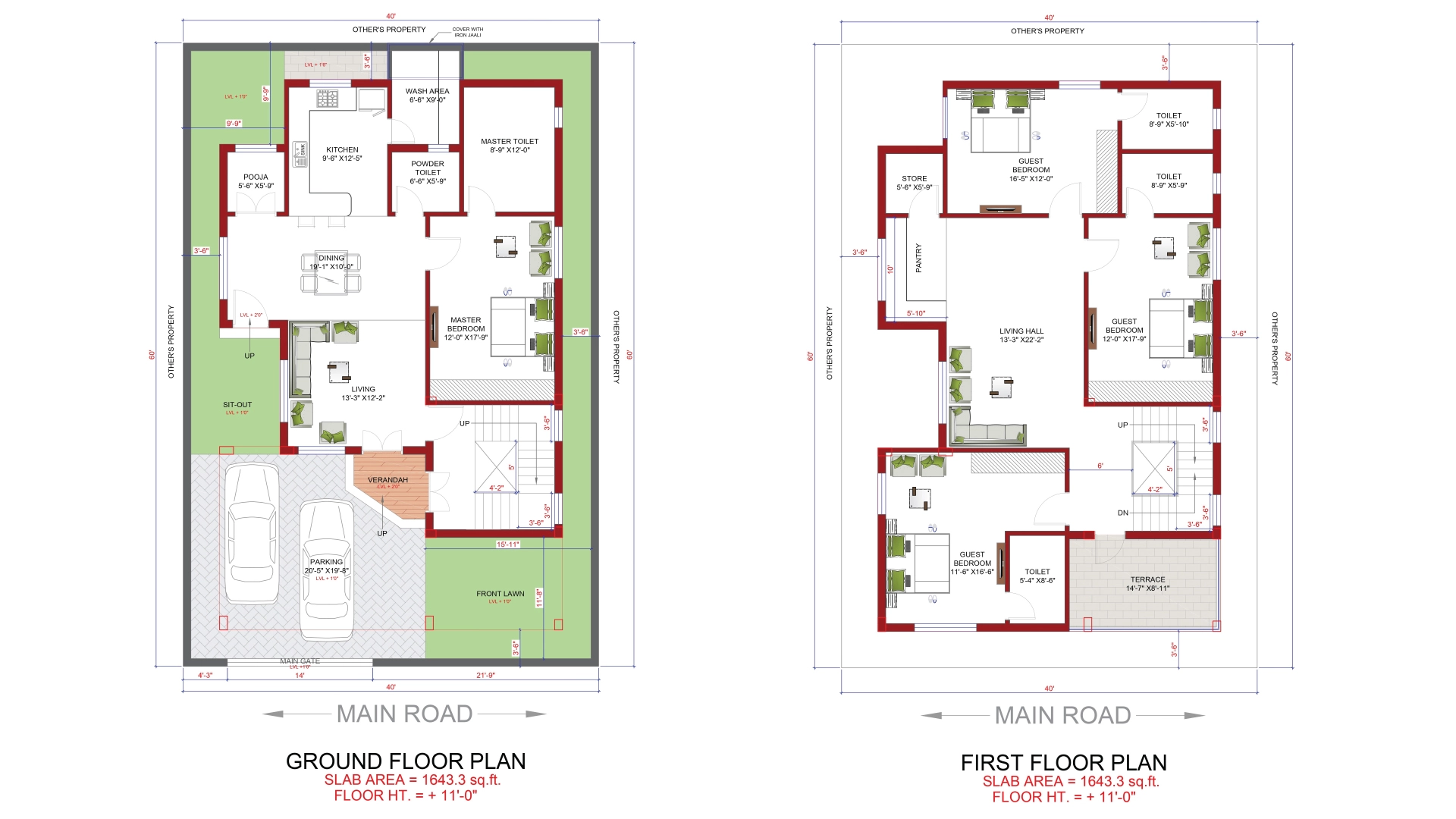
Commercial
Commercial floor plans cater to businesses and public spaces. They encompass offices, retail stores, restaurants, and more. Efficiency, branding, and customer flow are key considerations in commercial floor planning.
Landscape
Landscape floor plans focus on outdoor spaces. They detail features like gardens, patios, pathways, and plant arrangements. These plans integrate nature with the built environment.
Creating a Floor Plan
Initial Design and Conceptualization
Begin by visualizing the purpose and function of the space. Consider traffic flow, room relationships, and the overall feel you want to achieve.
Measuring and Drawing to Scale
Accurate measurements are vital. Measure the dimensions of the space and convert them to a suitable scale for your floor plan. A common residential scale is 1/4 inch equals 1 foot.
Adding Details Step by Step
Start with basic structural elements like walls and doors. Gradually add furniture, fixtures, and annotations. Use consistent symbols and labels for clarity.
Interpreting House Floor Plans
Understanding Symbols and Annotations
Learn to decipher the symbols used in floor plans. Common symbols include circles for light fixtures, “X” for electrical outlets, and dashed lines for overhead cabinets.
Navigating Room Layouts
House floor plans provide insights into how rooms are interconnected. For instance, bedrooms are grouped together for privacy, while common areas are more open.
Grasping Flow and Functionality
Consider how people will move through the space. A well-designed house floor plan ensures convenient access between rooms and a logical flow.
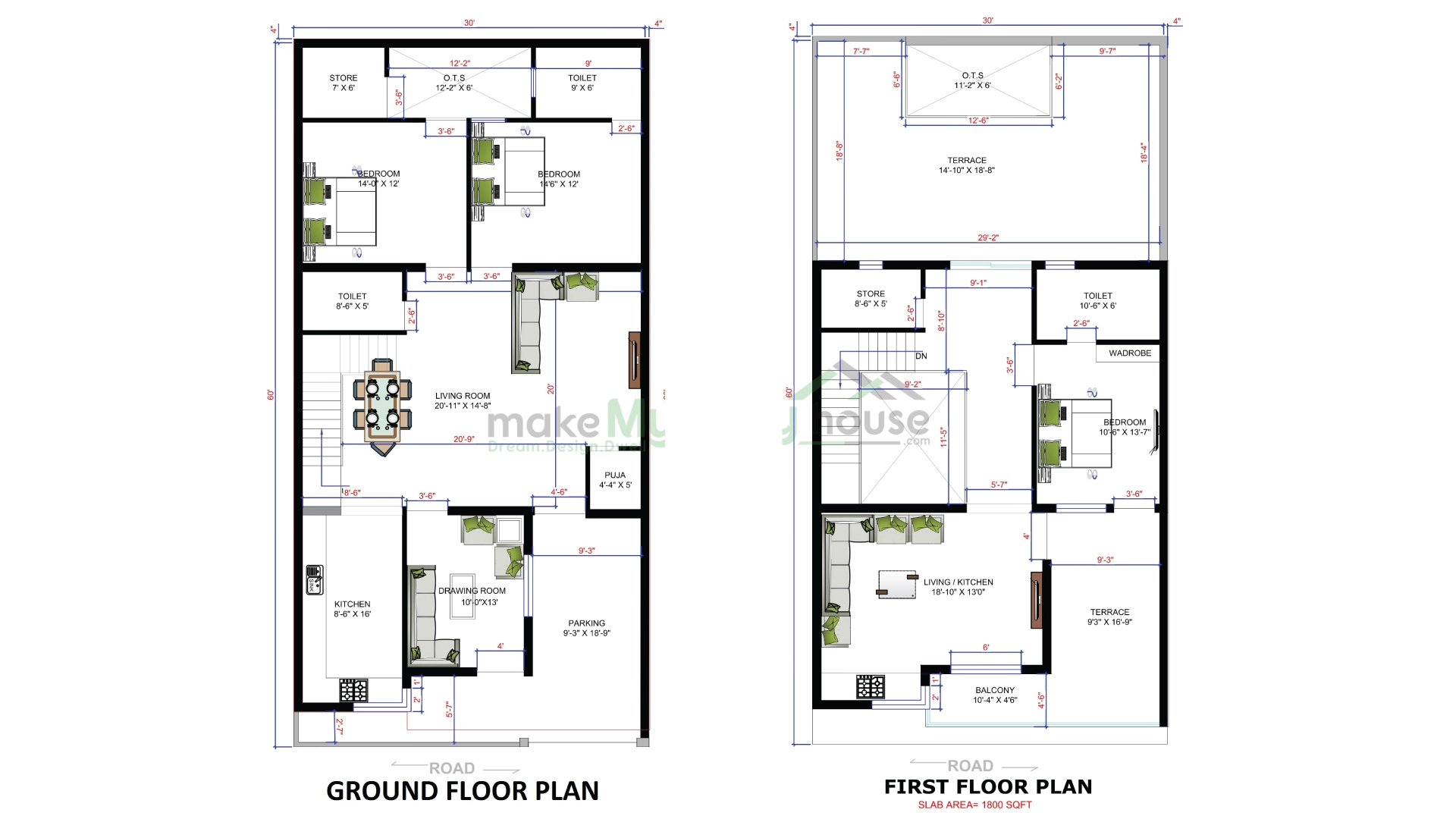
Advanced Tips for House Floor Plans
Incorporating Accessibility Features
Ensure your floor plan accommodates people with disabilities. Include features like ramps, wider doorways, and accessible bathrooms.
Optimizing Space and Traffic Flow
Maximize the use of available space. Avoid creating cramped areas or dead zones. Prioritize efficient traffic flow, especially in high-traffic spaces like kitchens.
Balancing Aesthetics and Practicality
While aesthetics are important, functionality should not be compromised. Strive for a balance between visual appeal and the practicality of the design.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Incorrect Scale
An inaccurate scale can lead to a layout that doesn’t match the actual space. Always double-check your measurements and chosen scale.
Overlooking Details
Small details like outlet placement might seem insignificant, but they greatly impact usability. Pay attention to these nuances.
Neglecting Future Needs
Anticipate potential changes in the future. A flexible floor plan can accommodate evolving needs, such as room conversions or additions.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of house floor plans is a valuable skill that empowers you to transform ideas into tangible designs. Whether you’re a homeowner, a design enthusiast, or a professional in the field, understanding these enhances your ability to create functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces. By grasping the components, techniques, and significance of house floor plans, you unlock the possibility of creating homes that more comfortable and truly align with your lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions about House Floor Plans
Q: Why are house floor plans important?
A: Floor plans are crucial for architects, designers, builders, and homeowners as they provide a clear understanding of the spatial relationships and flow of a building. They guide construction, interior design, furniture placement, and overall functionality.
Q: How can I create a house floor plan?
A: You can create a house floor plan using various tools, both traditional (like pen and paper) and digital (such as software applications like AutoCAD, SketchUp, or online platforms that offer pre-made templates).
Q: What are the key elements of a house floor plan?
A: Key elements include room dimensions, wall placements, door and window locations, circulation paths (hallways, staircases), furniture arrangement, and notes about materials and finishes.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when designing a floor plan?
A: Common mistakes include inadequate circulation space, improper furniture placement, ignoring natural light sources, and not considering future needs (such as expansion or changes in family size).











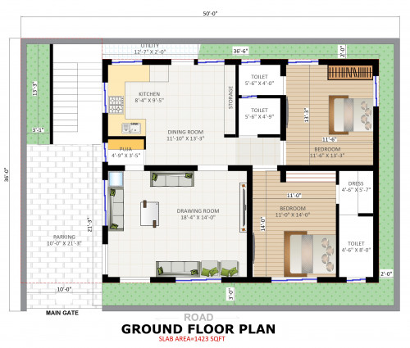
One thought on “A Comprehensive Guide on Mastering the Art of Floor Plans”